Repository containing a simple example of the Behavior Stack
The stack is partitioned into different layers of abstractions, each addressing different concerns; the separation of the layers allows level-specific efficient solutions. The number and separation of the layers are the subject of controversial discussions; in this example we use the abstraction layers defined by the RobMoSys Robotic Software Component Following the abstraction above, we categorize the robotic software in:
-
Task Layer, the layer where we design how the robot accomplishes a goal, disregarding the implementation details. In this example, it describes the a Behavior Tree (BT).
-
Skill Layer , the layer where we design the basic capabilities of a robot (e.g. grasp an object); It describes the implementation of a leaf node of a BT that that can run in mainly two fashions with respect to the BT engine:
-
In the same executable, where the source code of the skill is written inside a leaf node of the BT engine that implements the Tick() and (for actions) the Halt() methods.
-
-In a separate executable, where the source code of the skill is written in a separate program that exposes the interface for calling the Tick() and (for actions) the Halt() methods. Over the network. A leaf node of the BT engine forwards the calls to the corresponding executable.
A middleware usually handles these calls over the network.
-
-
Service Layer, the layer that contains system-level entities that serve as the access point for the skills to command the robot (e.g. move mobile base destination, read sensor input); It described the server side of a service called by a skill to perform its basic capability (e.g. get battery level).
This example contains:
run_bt: An executable that runs a Behavior Tree (a task).
SimpleCounter: An executable that implements a counter and exposed 3 services, implemented as YARP Remote Procedure Calls: one to increase, one to decrease, and one to reset the counter.
ActionExample A skill that when starts request to SimpleCounter to increase the counter by 1 every second. When the skill stops, it resets the counter.
ConditionExample: A skill that when starts request to SimpleCounter its counter value and returns to the BT on a success state if the counter is lower than 10; it returns a failure state otherwise.
The skills ActionExample and ConditionExample are implemented in three ways:
-
As leaf nodes in the BT (In the same executable of the BT).
-
As YARP RF Modules (in a separate executable).
-
As State Charts, using the QtSCXML engine (in a separate executable).
- YARP
- BehaviorTree.cpp
- Groot (For behavior trees visualization, optional)
- GammaRay (State Chart visualization, optional)
Install Dependencies:
-
YARP: More information here.
sudo apt-get install cmake libace-devgit clone -b v3.6.0 https://github.com/robotology/yarpcd yarp && mkdir build && cd build && cmake .. && makesudo make install# Optional NOTE! this installs the library system wide -
Behavior Tree.cpp: (use a specific commit) run :
git clone -b 3.6.1 https://github.com/BehaviorTree/BehaviorTree.CPP.gitThen install the library:
cd BehaviorTree.CPPmkdir build;cd buildcmake ..makesudo make installNOTE! this installs the library system wide -
Groot: Follow the instructions here.
-
GammaRay:
add the following ppa :
sudo add-apt-repository -s -y ppa:robotology/testsudo apt install -y \ gammaray \ gammaray-plugin-quickinspector \ gammaray-plugin-statemachineviewer
Clone and compile this library:
git clone https://github.com/hsp-iit/behavior-stack-example
mkdir build;cd build
cmake ..
make
Go to the bin directory:
cd bin
and run the following executables:
./simple_counter./run_bt --from ./BT_leaf_nodes_example.xml
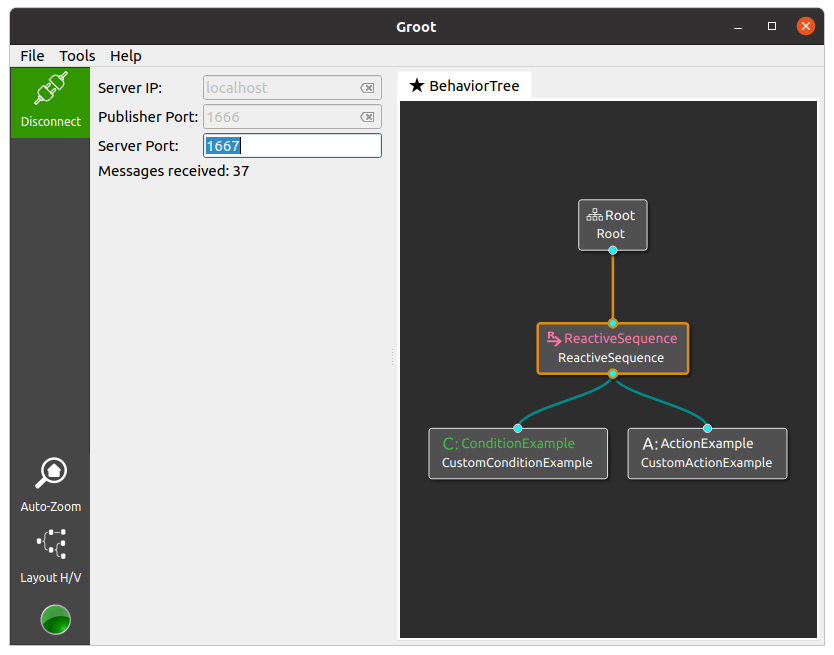
If you have Groot installed, execute it in "Monitor Mode" and then click "Connect" to see the execution of the BT, as in the figure below
Go to the bin directory:
cd bin
and run the following executables:
./simple_counter./rf_module_condition_example./rf_module_action_example./run_bt --from ./BT_rf_modules_example.xml
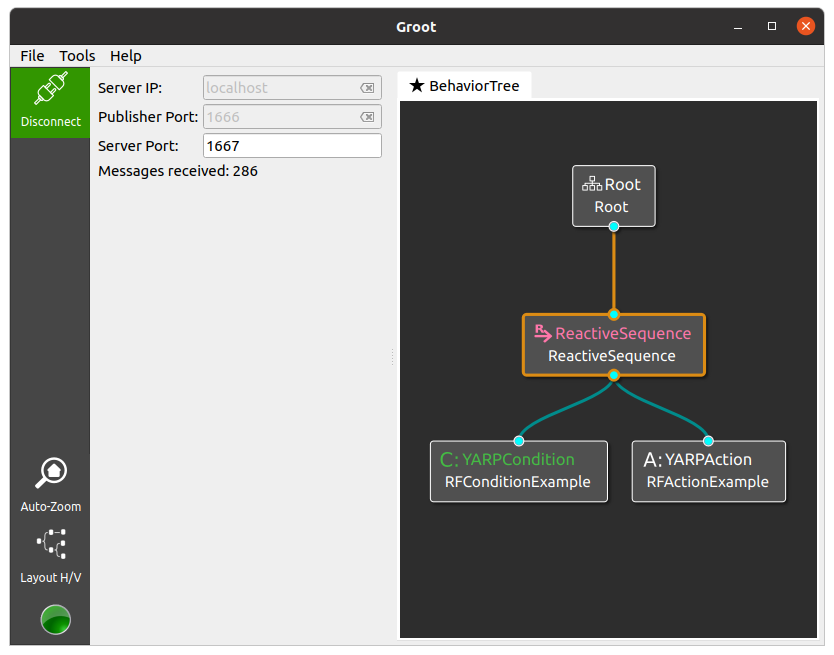
If you have Groot installed, execute it in "Monitor Mode" and then click "Connect" to see the execution of the BT, as in the figure below
Go to the bin directory:
cd bin
and run the following executables:
-
./simple_counter -
./state_chart_condition_example -
./state_chart_action_example -
./run_bt --from ./BT_state_charts_example.xml
if you have GammaRay installed, run the executables 2. e 3. as:
gammaray ./state_charts_condition_example
gammaray ./state_charts_action_example
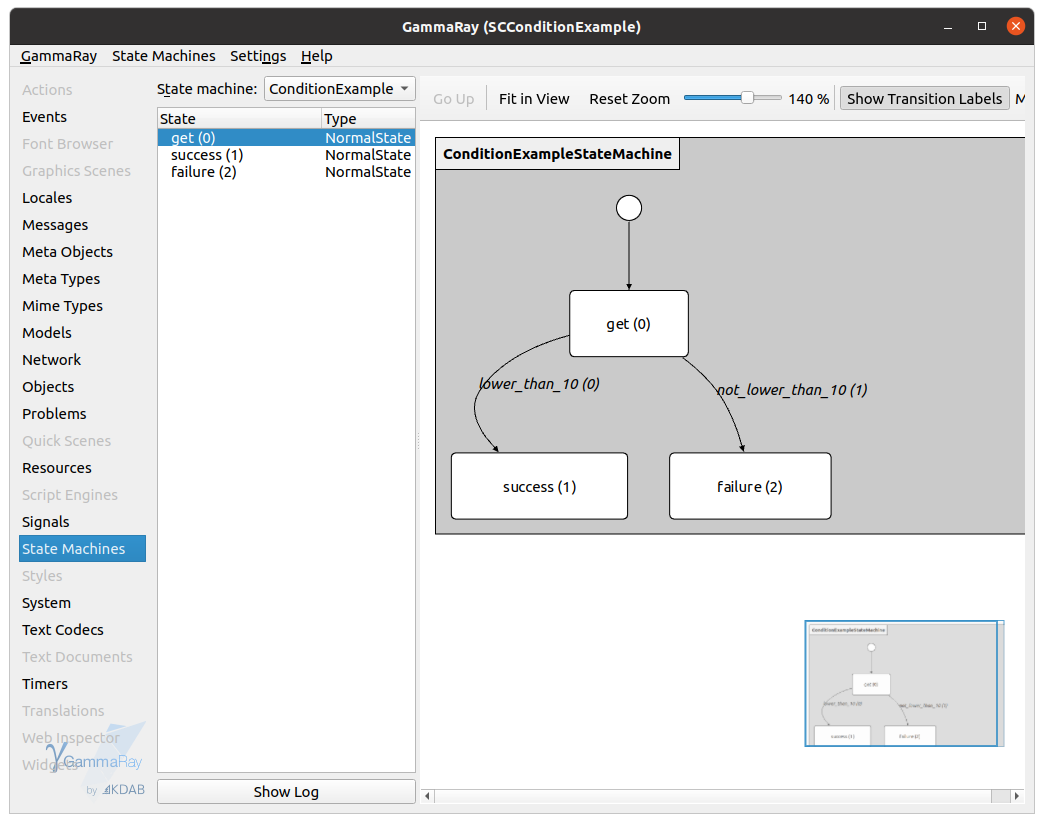
and then select the tab "State Machine" to see the execution of the skill, as in the figure below:
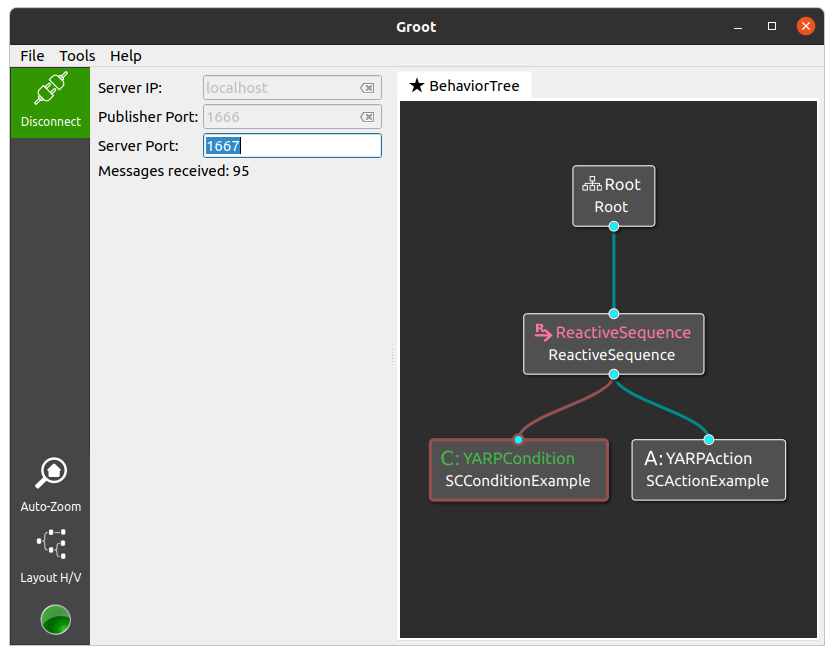
If you have Groot installed, execute it in "Monitor Mode" and then click "Connect" to see the execution of the BT, as in the figure below